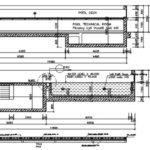
In this beginner’s architecture guide is the isometric drawing technique. Develop a set of skills that make your drawing different and give it a proper 3D-like look. It is make for designers and architects.
Isometric drawing surpasses the abstract nature of an art form since it is the fusion of art, mathematics, and technical design. Isometric drawing is one of those visual tools that plays a crucial role for every architect and engineer as it bridges the imaginary and concrete spaces.
In short words, what an isometric drawing is, and what peculiar function it is attribute to? What follows is a complete guide on isometric drawing, unveiling the history and essence of isometric drawings, the creating process, and the influence of isometric drawing in the USA’s professional engineering and structure fields.
What is the isometric drawing?
Isometric drawing is one of the types of 3D drawing that it enables to display an object that actually has three dimensions on a flat plane. Unlike perspective art which has different depths and sizes on the horizontal, vertical, and depth axes as they appear flat, isometric art are equal shortening of the axes.
This simplicity in explanation tools provides a straightforward and clear insight into the complexity. This therefore makes the design process more logical, accurate, and easy for designers and engineers to understand, show and prototype even the most complex ideas.
In contrast to how perspective drawings give the visual illusion of scaled objects seen at different distances, isometric drawings maintain the parallel nature of lines and provide a clear view that creates the idea that objects are true to scale.
This will be particularly useful for the development of technical applications since, in most such cases, precision and clairvoyance are a must.
Understanding Isometric Architectural Drawings
An isometric drawing is the three-dimensional representation of an object while it is observed from some limited angles in its proper scaling. It represents the very idea of a complex correlation between multiple dimensions in a simple way.
The word ‘isometric’, which comes from the Greek “isos” and “metra”, contextualizing it, represents precisely what things look like in the real world.
Isometric drawing is used for different primary purposes, from sketches of initial concepts to preparation of detailed construction documentation.
It’s an essential competitive skill in the architectural domain, where specific cutting-edge spatial comprehension is pivotal. Having the skills to create and understand the relationship between isometric drawings is beneficial, for instance, in the manufacturing and piping industries and civil engineering.
Key Features and Elements
Accuracy in the architectural isometric drawing is achieved through careful attention to detail and dedication to following the given features and rules. The plotting angle for each line is set up for a 30-degree inclination so that no line axis, be it the X, Y, or Z, goes diagonally across. Parallel lines will remain parallel, so the picture is accurate.
This also means that the three dimensions of an object are correctly represented. The axis lengths are equal and symmetric to achieve better visualization of the subject and its geometric accuracy.
Isometric projection offers a diversity of points of view as the object is represented from different sides. Those comprise three perspectives: the isometric top view, which sees the object from above; the isometric left view, which is an oblique angle from the object’s left side; and the isometric right view from the right side.
Each view represents the object by its measurements according to the respective orientation for motion in several directions around the axes.
The Advantages of Isometric Drawing in Architecture and Construction
Working on the isometric drawing, which allows us to visualize a project in 3D in detail, the revolution of architectural and engineering projects is now possible with precision, clarity and linking concept-reality.
Improved Visualization
One of the significant benefits of isometric drawing is that it is easy to imagine the structures or components in three dimensions since you do not need to deal with any space limitations.
This visibility is critical as it results in the later problems not going undiscovered, even though the design flaws may seen in the 3D version. Moreover, it will inspire fuller appreciation and knowledge about the project among the stakeholders, ensuring nobody has a different design concept of what the project should be.
Enhanced Communication
Isometric drawings serve as the vernacular that architects and engineers all over the world use. Such drawings function to overcome language barriers, which, as a result, increase the level of understanding, especially when we have to deal with large projects that include teams from different countries. Thus, they make continuous explanations to the clients and fellow investors, such that a project and its overall scope and ambition become more apparent to the viewer in a more intricate manner.
Efficient Planning and Design
The contribution of isometric drawing to the planning and design periods is quite noticeable. It enables a complete analysis of all factors, such as materials and site allocation. The helps simplify manufacturing process and ultimately reduces production time. It gives us a comprehensive perspective as we continue to observe and think critically about every aspect of the project, from tiny details to the big picture.
How to Draw in Isometric View
Start with the isometric grid, comprising equilateral triangles representing the three-dimensional space on a two-dimensional plane. As soon as the grid has been made, carefully draw the object in place, considering the 30-degree rule for angles.
The object is built gradually, and in this process, keeping the sizes correct will make an excellent isometric drawing in the end.
Pencil and paper may enough for freehand isometric drawings; however, software like AutoCAD or SolidWorks should be preferred if you are looking for more precision and speed. These programs carry out the isometric drawing journey, using measurements and replacing the physical calculations.
Tools and Software Recommendations
The use of isometrics drawing tools by beginners can expedite the rate at which they learn. The use of isometric graph paper drawing and specialized templates assists in creating the initial understanding of isometric drawing. From a software perspective, Autocad, Revit, and Solidworks are the industry reference standards with a complete set of 3D drawing and modeling tools, including isometric capabilities.
Isometric Drawing In AutoCAD
In AutoCAD, Isometric Drawing tools a very powerful utilizing relevant functions for developing intricate designs. The AutoCAD becomes known for 2D and 3D drafting. Isometric drawing tools are made especially for it.
It is pretty-easy-because-bedrock, correct, and persistent projections of complex structures. Users can orient themselves through 2D and isometric views being support by an isometric grid which does not let them lose precision and think of the directions between coordinates.
A snap feature of AutoCAD is the snapping that assures the comp to perfectly aligned hence increasing the clarity of drawings. It is the new advanced technology that enables us to make our designs more accurate with textures, colors, and light effects.
It enables the creation of a more realistic and design ideas presentation. Through this, the audience can better connect with the design process. Isometric drawings in AutoCAD are precisely made, clearly communicative, and documented in architecture and engineering when drafting plans for buildings or bridges.
Isometric Drawing In Revit
Incorporation of Isometric Drawing for Revit converts 3D models for designing in both architectural and engineering projects through the implementation of the isometric drawing principles.
In Revit, which is a known building information modeling software, we entirely can build elaborate and multi dimensional building models that give a one-look translation of the 3D view. Through this integration, the accuracy level is increase greatly thus the risks are minimize to give a whole viewpoint of the project.
Professionals not only enjoy producing isometric drawings directly from 3D models, but this also increases the speed of work and frees them from errors before them when they draft manually. An isometric is utilizing to represent 3D views.
This is to maintain a degree level of accuracy. Information is store in the data in Revit which includes material lists, dimensions, and costs and that’s what simplifies the processes of project planning.
Acquisition of the skills in Revit made it feasible to automate the isometric drawings’ production thereby bringing efficiency in workflow as well as achieving more successful outcomes of the projects and the process of communication involved with stakeholders in the construction and design.
Examples of Isometric Drawings in Architectural Design
Isometric drawings are not appliy only in architecture and engineering but also in many different fields.
Types of Isometric Drawing Examples
The ‘Isometric top view’ can utilized for cityscapes or floor plans, such as the isometric view of an office space showing the furniture placement.
It could be an elevation depicting wall details, including doors and windows. The ‘Isometric right view’ could be exemplified by a drawing of a building exterior to show form and massing.
Showcase Real-World Applications
Isometric drawings are integral to the construction of significant architectural projects, from bridge construction to skyscrapers. One real-life example of this is the stage of concept development of a sports stadium, where isometric drawings help locate seats, support columns, and entry points.
Highlight Successful Projects
Celebrating accomplished projects may be proof in itself of isometric drawing’s importance to actual architecture. A relevant example is the use of isometric drawings in building a hospital that facilitates the arranging of complex medical equipment and spatial arrangement for patients and staff’s movement patterns, as well as the integration of technology systems.
Tips for Mastering Isometric Drawing
To know how to do something, you have to do it—structured physical experiments like drawing a sequence of cubes and spheres in isometric form help to improve aptitude for that.
However, knowing about the frequent slip-ups, for example, an incorrect angle measurement or a wrong line placement, it is crucial to understand their role in the process and to learn how to avoid them since even the slightest error can ruin the drawing’s accuracy.
Conclusion
The control of orthographic draft is a skill as accurate as the buildings that it assists in imagining. Its application in architecture and engineering is comprehensive, thus providing an opportunity to envision without any ambiguity. Learning or using isometric drawing gives you more abilities to design, problem-solve, and communicate in the built context.
Our guide shall guide experts to the realms of isometric drawing, asking them to add this essential tool to their skillset and into their project toolboxes. The path to gaining an isometric drawing mastery is highly fulfilling and necessary, and it is through this that interesting geometry is born.