Quick Summary: Explore the fundamentals of HVAC systems, how they function, and the various types available, providing essential insights for anyone interested in home or commercial heating and cooling solutions.
Indoors, building owners and other professionals in architecture and build-up use HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, which people hardly realize as heroes of maintaining indoor climatic conditions.
They are the ones who are primarily responsible for ensuring that people live and work in a cooler, safer, and healthier setting. They are not only for the restful existence of individuals but also for historical significance, the latest technology, and other things that build them up for architects, house owners, and HVAC professionals.
In this blog, we have considered the complex technicalities of systems, analyzed their constituents and functions, listed the various types of systems, discussed their operation mechanism, and mentioned the factor that affects the cost of new designs. Besides, we go in-depth into their meaningful impact of them that creates altered qualities of indoor environments.
The Historical and Modern Significance of HVAC Systems
The idea of HVAC emerged in ancient civilizations when buildings that utilized natural ventilation and heating systems constituted the idea of houses.
The past has caught up with the speed of modern times, and HVAC has become an essential part of buildings during design and construction. Step by step, the HVAC systems become more and more advanced, making it possible to exercise more precise control over the environment’s indoor parts while saving energy.
Nowadays, within the context of modern architectural design, the HVAC system has become very sophisticated and highly responsible for providing the necessary conditions for the overall energy efficiency of the building.
Implementing the above systems from the design stage facilitates the overall integration of aesthetic, functional, and enjoyable aspects.
What Is an HVAC System?
An air conditioning, ventilation, and heating system is a widespread form of a comprehensive network that provides air conditioning, ventilation, and heating products for residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
Its overriding purpose is to create pleasant considerations regarding indoor environment quality and thermal comfort for occupants. The operation of the heating, ventilating, and air conditioning system is unified; every functional air is a separate link that enables the system to reach the intended air conditioning.
Heating: This element is accountable for creating warmth in buildings mostly through instruments like furnaces or heat pumps. These devices also transfer energy – frequently from gas, electricity or green sources – into warm air, then send the latter throughout the environment.
Ventilation: Stripping and flushing the air with fresh air helps to control heat, replace oxygen, and remove water vapor, odor, smoke, carbon dioxide, dust, air contagions, and carbon dioxide.
This is the case, as ventilation is the critical factor for keeping indoor air quality at safe levels and preventing stale air no longer filled with oxygen.
Air Conditioning: Unlike heating, air conditioning takes warmth and humidity from the indoor air and thus acts as a comfort system during summer.
Using refrigeration, air conditioners achieve this by withdrawing the heat from indoor air and letting out hot, purified air to the outside while incorporating fresh, cool, and dry air inside.
Manipulating the complex set of HVAC system functions is defined by the principle that each feature is essential, and their equilibrium to establish the perfect indoor atmosphere is required.
Several alternatives were available, including the construction of new buildings or retrofitting existing ones, which are all part of achieving sustainability and comfort in the built environment.
However, the implementation of HVAC, which led to the emergence of energy-efficient and innovative solutions, remained at the forefront.
The HVAC Foundations: Understanding How HVAC Systems Work
At the basic level, HVAC systems (the abbreviation for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) are competently developed to handle air conditioning within a building’s confines. An intelligent blend of air circulation, precise temperature regulation, and extensive filtration processes simultaneously achieve the objectives of these systems.
Key elements such as furnaces which help to provide heating, heat pumps that can offer both cooling and heating and air handlers whose job is to move air from one point to another, and ductwork, which are channels where conditioned air flows, all work in coordination to ensure proper and safe indoor condition.
It is only possible to diligently appreciate the intricate nature of HVAC systems by first understanding heat transfer, fluid dynamics, and thermodynamics. Heat transfer is the process of heat moving from one place to another, which is one of the pivotal ways of raising the temperature or cooling the space.
In fluid dynamics, one can figure out how the air, which in this case is a fluid, moves and behaves inside the systems, which is fundamental for proper ventilation and air distribution. Thermodynamics, the science of heat, work, and energy, forms the basis for engineering systems that properly regulate energy.
Precision and efficiency in HVAC design and delivery are central to these basic concepts but also call for the constant refinement of technology in the industry to improve energy efficacy, emissions, and air quality. By unceasingly complying with these principles, HVAC systems could yield maximum comfort in a healthy environment that meets all occupants’ needs.
Fundamentals of HVAC System Components
The main components holding any HVAC system are these system core structures that jointly are the most important reason for creating competent heating, ventilation, and air conditioning.
Grasping these components of an HVAC system is important both for the professionals who install them and for the homeowners and building managers, as it allows for the system to operate efficiently, be repaired when a problem occurs, and then for any upgrading or replacement to be done in an educated way. Below are key components that constitute the foundation of HVAC systems.
Thermostat: The thermostat is the brain of the HVAC system because it is the equipment that controls the temperature that the users want the system to maintain.
It detects the current temperature and modifies the system to activate the cycle on or off the normal cycling process to achieve the set temperature. Modern thermostats come with programmable options to maximize the time the system is working and preserve comfort for the occupants after school and before work.
Air Return: This juncture is when the cycle of ventilation is initiated. The air return is responsible for drawing fresh air, expelling it through a filter, and finally feeding it into the system for heating or cooling. Frequently, the cleansing of the filters in the air returns is paramount to constant air quality as well as system effectiveness.
Filter: Located next to the air intake, the filter’s primary function is to trap dust, pollen, and other air stream Pollutants and prevent them from further cycling around the machine. Filters vary in type and efficiency from one model to another, and the right choice can be the critical factor for dust-free air quality and the health of the building’s occupants.
Heat Exchanger: The furnace is made up of the heat exchanger that is placed in the exhaust. This gives heat to the incoming air in the combustion chamber. It is a significant part of the heat exchanger that makes the air evenly warm on all the surfaces in the room. The design and the kind of operated heat exchanger material play a vital role in the heat exchanger’s performance and safety.
Blower Motor: Once the furnace heats the air, it forces the air into the ductwork, where it flows to bring the desired temperature to the building. Its speed and efficiency determine the device’s competence in retaining stable temperature units.
Cooling Coil/ Evaporator Coil: Seek it inside an air handler or on a furnace, the cooling coil not only cools but also drives out moisture. As the air flowing over the coil is passing through it, the circulating refrigerant behaves as a kind of heat pump, sucking heat out from the air to cool it down. Cooling is what keeps the units pristine in the summer.
Compressor and Condenser Coil: The outdoor sections of the existing system are either air conditioners or heat pumps. In this process, the compressor circulates the refrigerant in the loop while the condenser coil expels the heat outside that has been separated from the indoor air.
Ductwork: The ductwork usually has a web of tubes that distribute warm or cold air from the heat exchanger to different rooms. However, properly designing and installing ducts and sealing are also important factors in preventing energy losses and ensuring efficient air distribution.
Vents: Vents, as the one mechanically controlled pathway through which air heated and cooled in the system attains the interior rooms. They are seated with specific goals in mind to achieve whole air distribution and ensure that the interior air temperature and comfort of everyone stay constant.
Overall awareness of all HVAC components, their functions, and how they work together to ensure proper functioning within an HVAC system would form a firm ground for anyone interested in HVAC design, implementation, installation, or operation.
The acquirement of such expertise extends beyond suboptimal system operation, as it also encourages efficiency in energy usage and economy in the environment built.
Types of HVAC Systems to Suit Every Space
The HVAC industry is represented by its diversity and many approaches made every time. Different types could suit different structural configurations, occupancy utilization, and efficiency needs. Here’s a brief overview of the most common types:
Central HVAC Systems
Central heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems (HVAC) deploy carefully planned ductwork to coordinate air outflow from the central machinery to areas along the building’s interiors. Being most effective in much bigger buildings and corporate offices they commonly offer set temperature conditions as constant and stable.
The core unit can be a single entity connected to an extensive system or even a series of smaller systems working together (all wired to a more comprehensive system or individually).
Split HVAC Systems
Split systems are the most common unit with rear and exit covers. The evaporator coil housed in the indoor unit is responsible for transferring the fluid within the system. The outdoor unit, meanwhile, has the condensing coils and the compressor. These systems are highly adaptable candidate technologies in many building types mainly due to their ability to provide efficient heating and air conditioning.
Ductless Mini-Split Systems
Like split systems, ductless mini-splits (DMS) have no ductwork, instead have multiple indoor units linked to a standard outdoor unit among them. They provide the ability to zone the heating and cooling features for separate spaces, therefore they become one of the most adequate heating systems for add-ons and spaces without ducts.
Packaged HVAC Systems
What is most distinctive about packaged systems is that all parts are in one place: the cabinet, which is usually placed outside or in a crawl space. They are often found in kitchens with restricted office space; they are also heavily applied to commercial work areas.
No type of HVAC system is absolute, thus, all of them have unique advantages and disadvantages. Selecting an optimum HVAC system customized to suit the needs of a particular building carries the most significant weight.
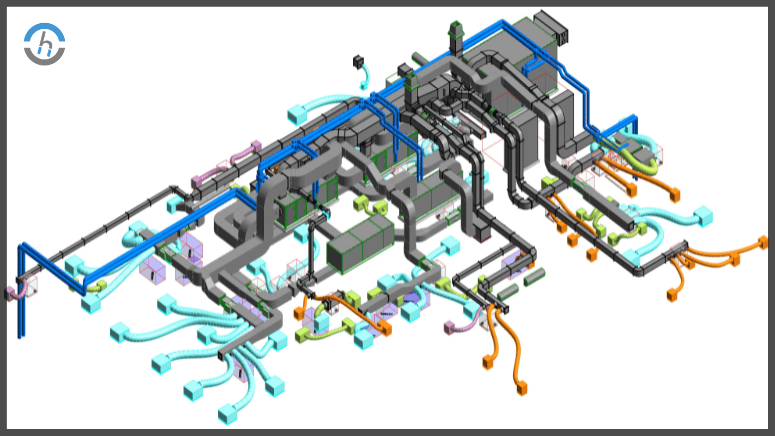
The Crucial Role of HVAC Drawings in System Design
An accurate and more elaborate HVAC drawing provides the basis that leads to the rise in efficiency of the systems under consideration. Such specific representation offers a visual grid to all parties, including architects, engineers, and HVAC technicians, to ensure the system installation and interfacing with the building structure are performed correctly.
The efforts of precision measurements, calculations, and accurate building regulations adherence underline the production of HVAC drawings. Consulting the knowledgeable companies providing HVAC drawings reassures that pricey errors are minimized and the project time is efficiently executed.
Benefits of a Well-Designed HVAC System
Advantages in Time and Energy Saving, Productivity, Good Indoor Air Quality, Sustainable, and Eco-Friendly, Creating a Comfortable Ambience, and Minimising Harmful Impacts on Occupants Health.
An adequately arranged HVAC system provides more than just warmth in the interior, it keeps the air quality good inside and energy saving. Thanks to high-performance components, sound isolation, and advanced control systems, modern climate-controlling systems of buildings eradicate significant emissions and diminish run costs.
For residential areas, a peaceful and livable environment with always keeps healthy and fresh may be an excellent pedestal for human living. Commercial and industrial facilities benefit from robust systems that can handle large-scale heating and cooling demands without compromising on performance.
Exploring Future Trends in HVAC Technology and Design
Explore the novelties in HVAC technology and forecast changes in the design trends that will prevail in the near future of heating, ventilating, and air conditioning. Be a pioneer in the HVAC field with the latest news on modern technologies. Attention: Use this sample sentence to introduce the topic of channel strategy and how it helps businesses reach their target market effectively.
Like others, the HVAC industry is approaching sustainable practices because of the eco-consciousness growth. Grеener technologies for heating and cooling systems, temperature control, smart thermostats, and several other technologies are increasingly gaining popularity among designers globally, setting trends and contributing to reshaping architectural outcomes.
With the BIM and AIS integration now making the construction process more accessible, there is another trend that is smoothing the process. The application of BIM makes it possible to perform the virtual constructions of structures for demonstrating the clash detection of HVAC equipment to facilitate their inclusion into the building design from the start.
Innovative HVAC systems that can make adjustments choosing from user behavior and settings automatically is the beginning of the next frontier and will be most convenient and energy-saving for users. These progressions are not only crucial notions for technicians but also for architects, whose aim is to build intelligent and eco-friendly structures.
Read also: Comprehensive Guide to HVAC Duct Shop Drawings for 2024
Choosing the Right HVAC Outsourcing Services
Selecting a good HVAC outsourcing service can make the entire HVAC system of the building run at a high efficiency, make it function better, and save energy as well. With the variety of choices in the world, Chudasama Outsourcing is one of the leading providers of professional HVAC drafting and drawing services. Famed for their superiority in precision, skill, and commitment to quality, Chudasama Outsourcing offers customized solutions that serve a wide variety of HVAC requirements around the world.
Their group of technologically advanced experts implements the latest technologies. It uses best practices to create exact HVAC plans, guaranteeing the integration of HVAC systems in projects of any magnitude and will be optimal in performance.
Here at Chudasama Outsourcing, we provide top-notch technical support, an uncompromising approach to meeting deadlines, and the highest standards of quality in all facets of designing and implementing Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of HVAC systems is a rewarding pursuit for homeowners seeking comfort and efficiency and for architecture professionals striving to deliver innovative and sustainable drafting designs. Via the deep knowledge of HVAC fundamentals, one can undertake decisions that directly interfere with the quality of the indoor livelihood and yet determine the broader environmental trends.
We now live in a climate-aware era and intelligent building technology. This situation has always been more important to supply. While we scan the horizon of even more sophisticated building environments, the comprehension of HVAC systems will be a sign of distinction in the overall success of architectural projects. This describes the future of very complex building projects.